As scientists and researchers continue to make advances in robotics, we have seen various kinds of robots performing advanced tasks. We have seen Boston Dynamics’ robots help the police solve crimes, monitor nuclear plants, and even dance to groovy tunes. Now, researchers have developed a new robot that can biologically reproduce to create offspring. Yes, you read that right! The new kind of robot uses a novel form of biological self-replication process to create its “children”.
Dubbed as Xenobots, these robots were recently detailed in a research study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. As per the authors of the paper, the Xenobots can gather hundreds of cells and assemble them into “baby” Xenobots that evolve and start their lives after a few days of being “born”.
“People have thought for quite a long time that we’ve worked out all the ways that life can reproduce or replicate. But this is something that’s never been observed before,” said Douglas Blackiston, one of the co-authors of the study, in a statement.
Now, how do the Xenobots reproduce? Well, it turns out that the millimeter-wide bots are developed using living cells from frog embryos. So, the living cells from frogs add reproductive capabilities to the non-living Xenobots. However, although a Xenobot can create offspring independently, the machine dies soon after the process. So, to help parent Xenobots see their children grow up, the researchers turned to artificial intelligence (AI).
The team of researchers used an evolutionary algorithm to simulate billions of body shapes to find out the most effective one for the self-replication method. Amongst others, the researchers discovered a Pac-man-like body shape that can use its “mouth” to compress stem cells into a circular-shaped “baby” Xenobot.
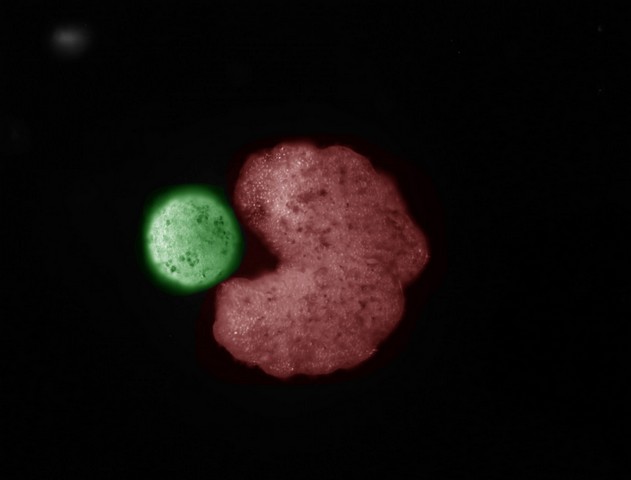
Now, coming to the application of the new discovery, the researchers are positive about it, though the technology can be used to create swarms of self-replicating robots that can destroy humanity! Well, that is going to be a long shot, however. Nonetheless, the researchers believe that their technology can aid various technologies, including living machines to clean up microplastics or develop regenerative medication. The possibilities are endless.
Credit: Source link




















