Summary: Ingested non-essential amino acids curb appetite and promote movement in mouse models.
Source: ETH Zurich
In experiments on mice, researchers at ETH Zurich show that non-essential amino acids act as appetite suppressants and promote the urge to move.
Their research is published in Current Biology and provides insight into the neural mechanism that controls this behavior.
Proteins can suppress appetite, so a protein-rich diet can help people lose weight. That’s just one of the reasons why this kind of diet has become increasingly popular in recent years. Working with mice, researchers at ETH Zurich have now demonstrated a new mechanism by which the building blocks of proteins—the amino acids—curb appetite. Specifically, it involves what are known as non-essential amino acids.
Of the 21 amino acids our bodies require, there are nine they are unable to produce on their own. They are called essential amino acids. Because we must obtain these through our diet, they have long been the focus of nutrition research. The other 12 amino acids are considered non-essential. The body can produce them itself by altering other molecules.
Shown in mice
It has been known that both essential and non-essential amino acids can suppress appetite. However, for the non-essential amino acids, the mode of action had not yet been demonstrated in living organisms.
Now, a group of researchers led by Denis Burdakov, professor of neuroscience at ETH Zurich, have shown for the first time in a living organism that the non-essential amino acids influence the brain in a way that curbs appetite and promotes exercise.
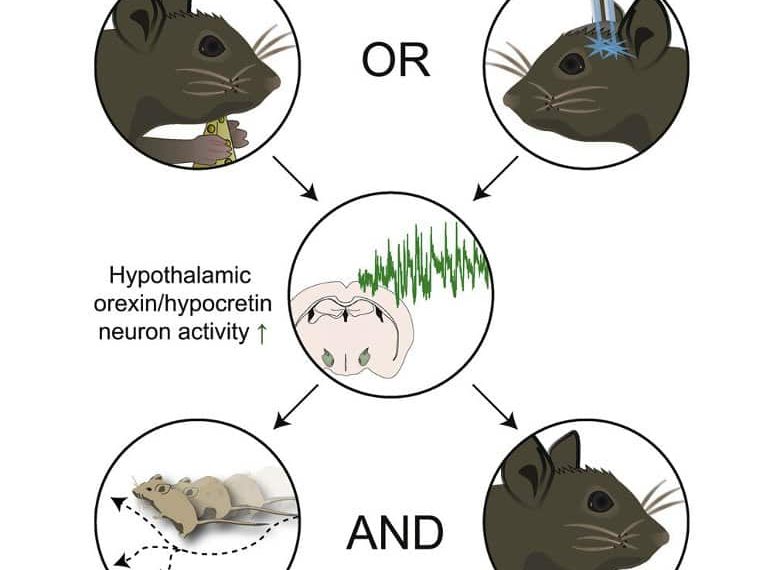
The researchers first fed mice either a mixture of various non-essential amino acids or a sugar solution with the same amount of calories (control group). Both groups of mice were then allowed to drink a milkshake, which they normally love.
While the control group drank copious amounts of it, the mice that had been fed non-essential amino acids avoided theirs. Instead, they went around their enclosure in search of alternative sustenance.
Rooted in evolutionary history
With additional experiments, the researchers were able to decode the underlying mechanism, in which specialized nerve cells in the brain—orexin neurons—play the main role. Proteins that the mice take in through food are broken down in the gut into their amino acids, which then enter the bloodstream. From there, the blood transports them to the brain.
The orexin neurons in the hypothalamus have receptors that specifically recognize the non-essential amino acids. In response, they initiate a neural circuit that produces the described behavioral changes.
This mechanism is likely rooted in evolutionary history. “Today, we have sufficient access to all nutrients, and we have plenty of time for eating. In prehistoric times, when this mechanism developed, that was likely not the case,” says Paulius Viskaitis, a postdoc in Burdakov’s group and lead author of the study.

“Back then, it was advantageous for individuals to spend only a short amount of time at a food source that consisted primarily of non-essential amino acids.” If eating non-essential amino acids promotes the urge to move, the animal will go in search of other sources of food—which potentially contain more essential nutrients and are more important for the individual.
Viskaitis stresses that the results are transferable to humans and other animals, as this mechanism affects a region of the brain that is very old in terms of evolutionary history and occurs equally in all mammals and many other vertebrates.
Still, for people who want to lose weight, a diet that includes especially many non-essential amino acids cannot be recommended across the board, Viskaitis says. Nutritional recommendations should be made on an individual basis, and they should also take health aspects into account.
About this appetite research news
Author: Press Office
Source: ETH Zurich
Contact: Press Office – ETH Zurich
Image: The image is in the public domain
Original Research: Open access.
“Ingested non-essential amino acids recruit brain orexin cells to suppress eating in mice” by Paulius Viskaitis et al. Current Biology
Abstract
See also

Ingested non-essential amino acids recruit brain orexin cells to suppress eating in mice
Highlights
- Ingested non-essential amino acids (nAAs) activate orexin cells
- nAAs or orexin cell optostimulation increases exploration and reduces feeding
- CCK-sensitive vagal afferents are not required for the nAA effects
- Orexin cell ablation abolishes nAA modulation of feeding and exploration
Summary
Ingested nutrients are proposed to control mammalian behavior by modulating the activity of hypothalamic orexin/hypocretin neurons (HONs). Previous in vitro studies showed that nutrients ubiquitous in mammalian diets, such as non-essential amino acids (AAs) and glucose, modulate HONs in distinct ways. Glucose inhibits HONs, whereas non-essential (but not essential) AAs activate HONs. The latter effect is of particular interest because its purpose is unknown.
Here, we show that ingestion of a dietary-relevant mix of non-essential AAs activates HONs and shifts behavior from eating to exploration.
These effects persisted despite ablation of a key neural gut → brain communication pathway, the cholecystokinin-sensitive vagal afferents. The behavioral shift induced by the ingested non-essential AAs was recapitulated by targeted HON optostimulation and abolished in mice lacking HONs.
Furthermore, lick microstructure analysis indicated that intragastric non-essential AAs and HON optostimulation each reduce the size, but not the frequency, of consumption bouts, thus implicating food palatability modulation as a mechanism for the eating suppression. Collectively, these results suggest that a key purpose of HON activation by ingested, non-essential AAs is to suppress eating and re-initiate food seeking.
We propose and discuss possible evolutionary advantages of this, such as optimizing the limited stomach capacity for ingestion of essential nutrients.
Credit: Source link