For several years now, every month 3Dnatives has given you the opportunity to discover a startup in the additive manufacturing sector. 3D printer and material manufacturers, software developers or machine distributors, many young companies are developing solutions that will impact the future of the industry. And as the end of the year approaches, it’s time to vote on who you think has been the most innovative in the additive manufacturing market this year out of our 3D printing startups of the month. Voting is easy: just go to the bottom of the article to select who you think deserves to be voted the 3D startup of 2021. And don’t worry, if you missed some of the companies shown during the year, we’ve prepared a summary below! The results will be announced on January 4th on 3Dnatives.
Vote Now For the Startup of the Year!
#1: ICON and 3D Printing on the Moon
Founded in 2017, ICON specializes in 3D printing of buildings. Since its first printed house in March 2018 in Texas, the American company has come a long way. Today there are no less than 20 buildings designed by ICON, while many projects are still in the works. Voted 3D startup of the month in January, 2021, the company is collaborating with NASA, among others, to realize an even more ambitious project. Together, the two companies want to 3D print buildings on the moon using regolith, a material from the lunar surface. To do this, ICON wants to use its gantry-type 3D printer called Vulcan, which is capable of printing up a house of up to 185 square meters with a material called Lavacrete. You can find the entire interview with the American startup HERE.
Crédits photo : ICON
#2: Addiguru and its Real-Time Monitoring Software for 3D Printing
In 2019, as additive manufacturing became more mainstream in several industries, Shuchi Khurana decided to launch Addiguru. In order to limit problems during the printing process and automate the production process, the 3D startup from February 2021 developed a software solution to monitor the manufacturing process in real time. However, in its early days, Addiguru’s software was only compatible with powder bed laser fusion. Designed to be easily added to other processes, Addiguru is currently working being integrated into fused deposition modeling (FDM) as well as DED. Read the full interview with Shuchi Khurana HERE.
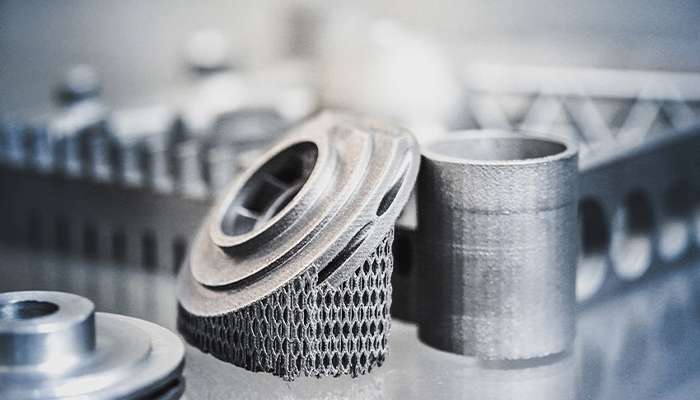

Photo Credits: Addiguru
#3: xolo and Volumetric 3D Printing
Based in Germany, the startup xolo is looking to disrupt UV curing methods with a volumetric 3D printing process. Called xolography, it offers a much faster manufacturing process, a smoother surface and more possibilities in terms of materials. As an example, the xube 3D printer, based on xolography, would be able to design parts in only 20 seconds for the smallest and 5 minutes for the largest. Compatible with the same photopolymers as SLA and DLP processes, xolo’s technology is currently aimed at the research world and should allow researchers to realize ideas that are not possible with conventional layer-by-layer printing. Find the full interview HERE.
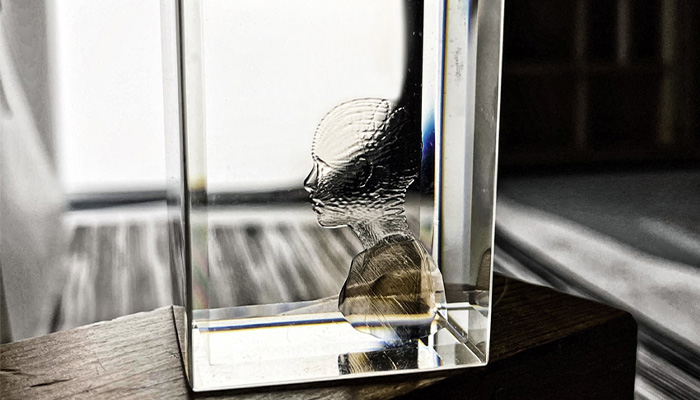

Photo Credits: xolo
#4: Mobile Smart Factory Promotes Local Manufacturing
After long months in the COVID-19 pandemic, many companies have been looking for solutions to transform supply chains. Among them was Mobile Smart Factory, a solution developed to support local manufacturing and provide parts on demand, leading to them being chosen 3D Startup of the Month in April 2021. Mobile Smart Factory is a modular factory enclosed in a container equipped with 3D printing devices. This “mini-factory” allows parts to be repaired and manufactured at any time, without the need for inventory or physical stock. The solution is aimed at industries located in remote areas with limited logistics capabilities. For example, it can be deployed in mines or oil and gas platforms. Johannes Schmidt, who is involved in the project, tells you more HERE.
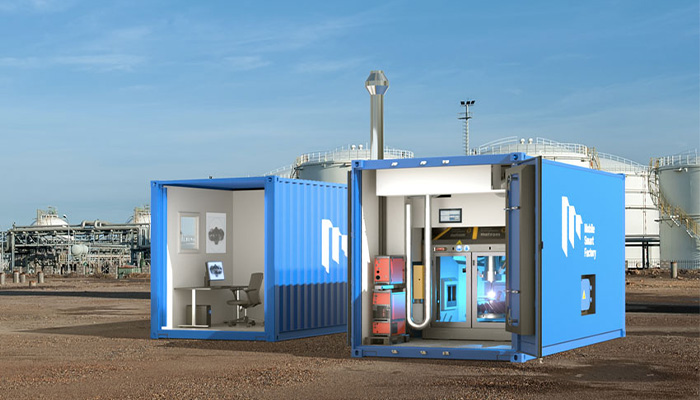

Photo Credits: Mobile Smart Factory
#5: One Click Metal Wants to Make Metal Additive Manufacturing Accessible to All
One Click Metal wants to democratize access to metal additive manufacturing by offering a printing solution that is easy to use and a powder system that is less complex to handle, all at a more affordable price. With machines based on laser powder bed fusion, One Click Metal is designed for all the companies, whatever their sector or their size. In order to differentiate itself from its competitors, the young company relies on solutions that accompany the user during each step of the printing process. Eventually, One Click Metal wants to make the technology accessible to everyone, in a single click. (Re)discover the interview with the German startup HERE.
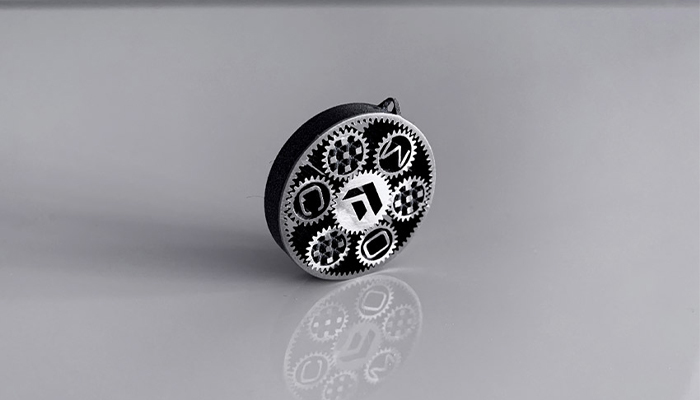

Photo Credits: One Click Metal
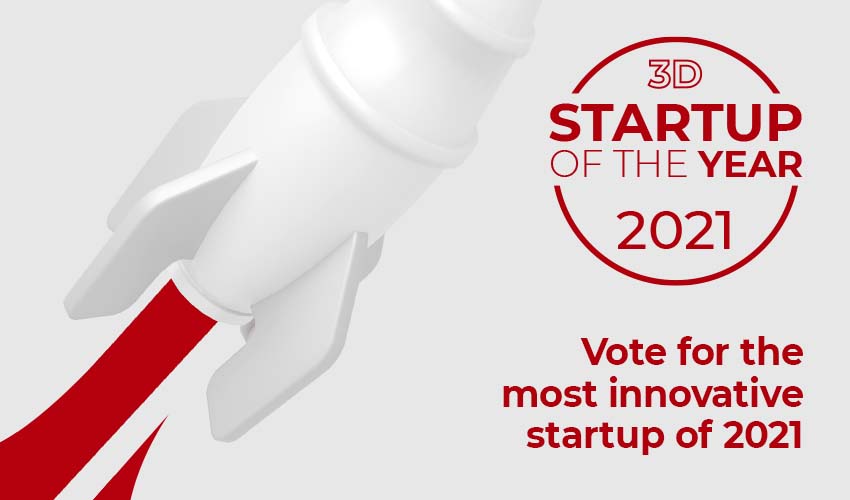
#6: Readily3D and its Tomography-Based Volumetric Printing Technology
Readily3D, a young Swiss startup, has developed a volumetric 3D printing method to create complex organic shapes in just seconds. As part of the European ENLIGHT project, the company has presented its first work on the pancreas. Using its technology, Readily3D was able to 3D print organic tissue from the organ. Able to solidify an entire object in one shot, the company’s 3D printer is compatible with a wide range of light-sensitive materials, such as acrylates, silicones and hydrogels. Through bioprinting, Readily3D hopes to produce organ parts on which rapid, controlled and repeatable tests can be performed. Find the full interview with the Startup from June 2021 HERE.
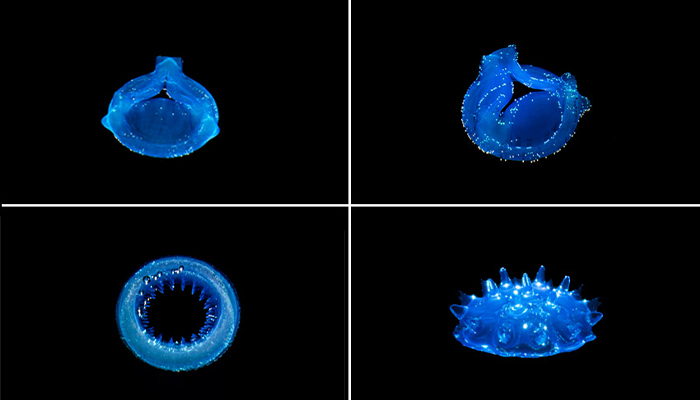
Photo Credits: Readily3D
#7: Handddle Structures and Industrializes the Uses of 3D Printing
Based in Bordeaux, Handddle is a French startup that helps professionals integrate additive manufacturing into their activities. It offers a micro-factory, called SmartFarm, capable of centralizing a fleet of machines, but also post-processing solutions. Designed to democratize 3D technologies, the solutions proposed by Handddle allow a complete control of the manufacturing process as well as a repeatability in all environments. The young company mainly targets companies with internal manufacturing needs and looking for automation. If you want to know more about Handddle and its solutions, you can read the full interview HERE.
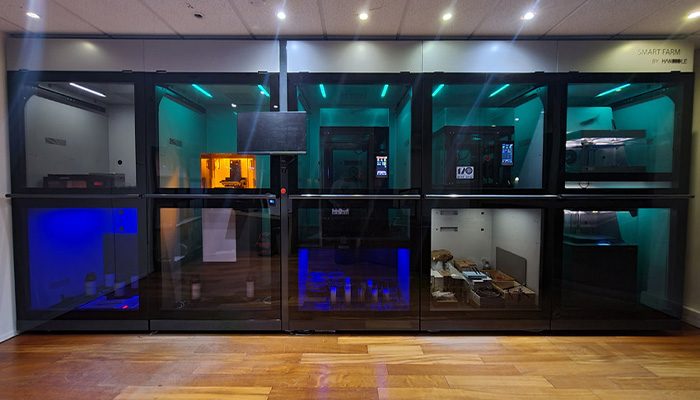

Photo Credits: Handddle
#8: Mantle and its Paste-Based Metal Additive Manufacturing Process
The startup Mantle made its grand debut to the general public by unveiling its TrueShape additive manufacturing technology. This metal 3D printing process differs from other technologies on the market in its ability to use a paste as the printing material. This method has enabled a whole new level of surface finish and precision. Ted Sorom, CEO and co-founder of Mantle, explains that TrueShape is a hybrid process that is both additive and subtractive, and parts made using this process do not require any post-processing steps. Sorom also notes that using a paste as the printing material offers better accuracy. We learned more about the startup in an interview from August 2021 HERE.
Photo Credits: Mantle
#9: ING3D and Mineral 3D Printing
Based in Germany, ING3D has developed a technology called Mineral Direct Laser Sintering (MDLS). Inspired by powder sintering, this 3D printing process allows the design of very light and non-flammable parts. In addition, MDLS reduces the cost of printing by a factor of 10 and speeds up the manufacturing process. ING3D’s technology consists of sintering light mineral materials, such as perlite, using a CO2 laser. Since this process does not require any additives, the raw material remains pure in form and can be disposed of without problems after the period of use. At the moment, MDLS is used in a variety of applications, such as furnace insulation and water filtration. David Manjura, founder of ING3D, tells you more HERE.
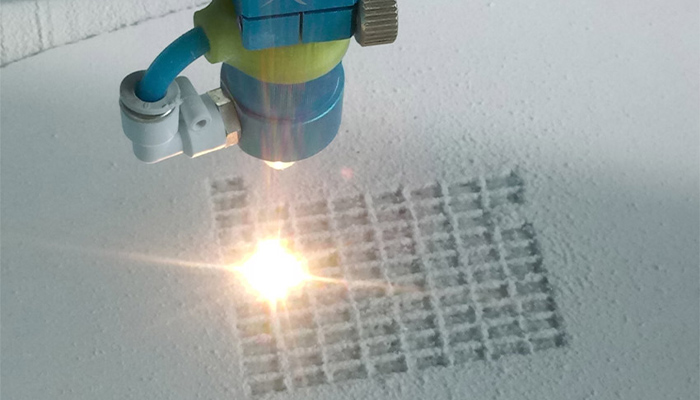
Photo Credits: ING3D
#10: Shapeshift 3D and its Customization Platform for 3D Printing
Shapeshift 3D, a Canadian company offering a platform for manufacturing personalized sports and medical equipment, was chosen as our 3D Startup of the Month in October. From scanning to printing, Shapeshift 3D’s software solution enables the manufacture of various products, such as orthotics, prosthetics and bicycle helmets. Optimized by artificial intelligence, the platform is able to help professionals. Once the 3D file is entered into the software, it automatically rectifies it and makes custom adjustments. In short, thanks to the advantages of 3D technologies, the Canadian start-up is able to provide its users with perfectly adapted parts. Check out the full interview with the CEO HERE.
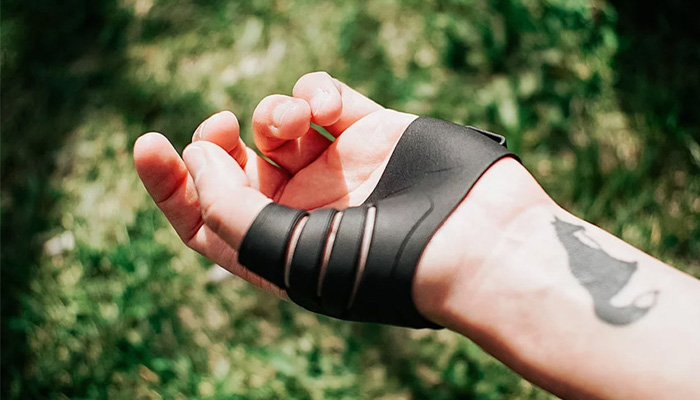

Photo Credits: Shapeshift 3D
#11: From Vases to Facades, Concrete 3D Relies on Concrete 3D printing
In the construction industry, more and more companies are turning to additive manufacturing. Among them is Concrete 3D, an Austrian startup that uses 3D printing to build all types of structures. The startup offers its customers 3D printed facade elements and home furniture. With the help of the technology, Concrete 3D offers its customers lighter but above all more durable constructions. 3D printing allows the company to use only the necessary amount of material, which significantly reduces CO2 emissions. Ultimately, the company wants to offer architects and other construction professionals new perspectives through 4.0 technologies. Michael Gabriel, division manager at Concrete 3D, looks back at the company’s technologies and ambitions HERE.
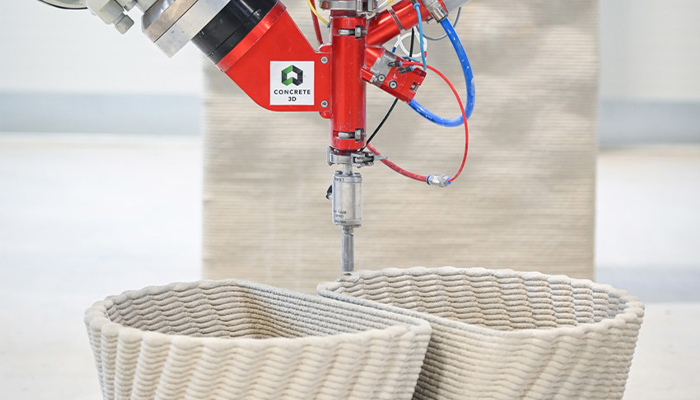

Photo Credits: Concrete 3D
#12: Exponential Technologies optimizes 3D printing parameters with AI
In order for companies to optimize processes and machine parameters as well as material composition, startup Exponential Technologies (xT) offers an artificial intelligence (AI) platform and search management system. Through machine learning, the startup hopes to drive mass adoption of additive manufacturing as a traditional manufacturing method. In particular, AI can be used to optimize machine parameters so that the machines perform as well as possible. Matthias Kaiser, CEO of xT, tells you more about the value of machine learning HERE.

Photo Credits : Exponential Technologies
Vote Now For Your Favorite Startup of 2021!
What do you think of the 3D startups of the month from 2021?
Let us know in a comment below or on our Linkedin, Facebook, and Twitter pages! Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly Newsletter here, the latest 3D printing news straight to your inbox! You can also find all our videos on our YouTube channel.
Credit: Source link